convert
| This command is experimental |
Definition
convert converts the string value into a numerical value.
Use one of the converting functions with convert:
The alternative option is to use evaluation commands. For example, strftime(), strptime() and tonumber() also converts string values into numerical value.
Examples
convert needs always one of the converting functions. If one of the converting functions isn’t used, an error will be shown.
Only one value can be added in a converting function. If you want to convert more than one table column, repeat the converting function.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval value1 = "1665561109", value2 = "1665561120"
| convert ctime(value1) ctime(value2)You can use wildcard with all converting functions.
| Currently, wildcard doesn’t work in DPL. This will be fixed before the community release. |
timeformat
timeformat specifies the format for the converted table column. It can be used with converting functions ctime and mktime.
If the time format hasn’t been specified, it will be shown as %m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval epochTime = 1664955774
| convert timeformat=%d.%m.%Y ctime(epochTime) as asciiTime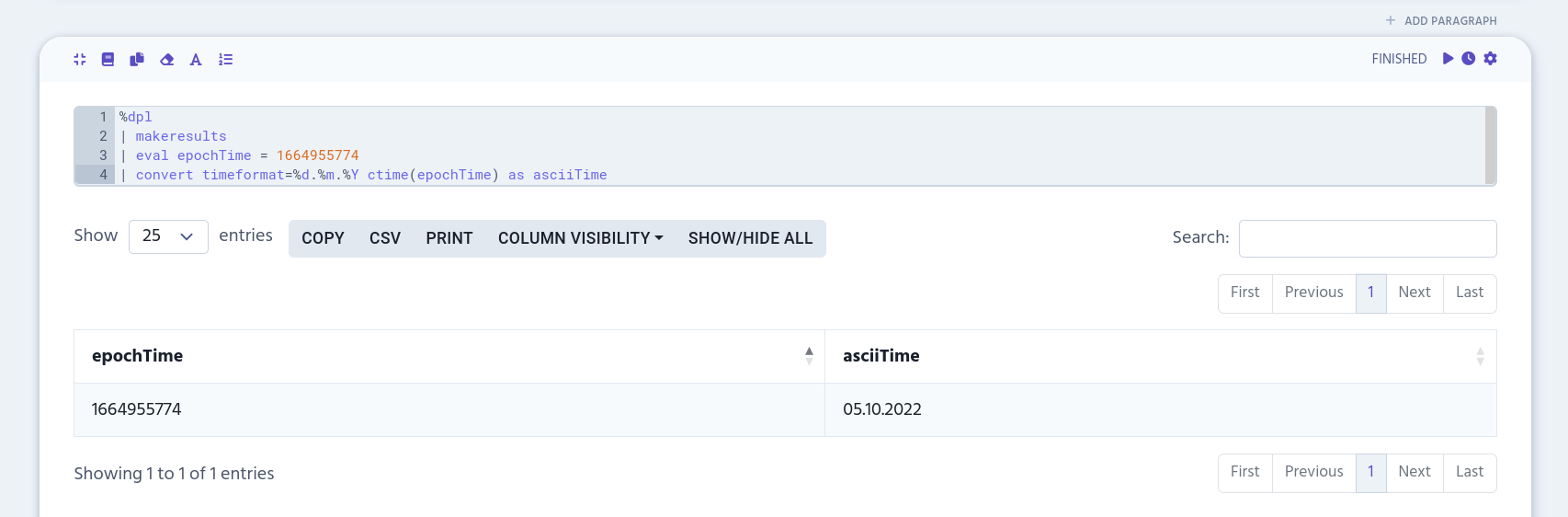
auto()
auto() converts automatically the table column by using the best conversion.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval value = 3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419716939937510
| convert auto(value)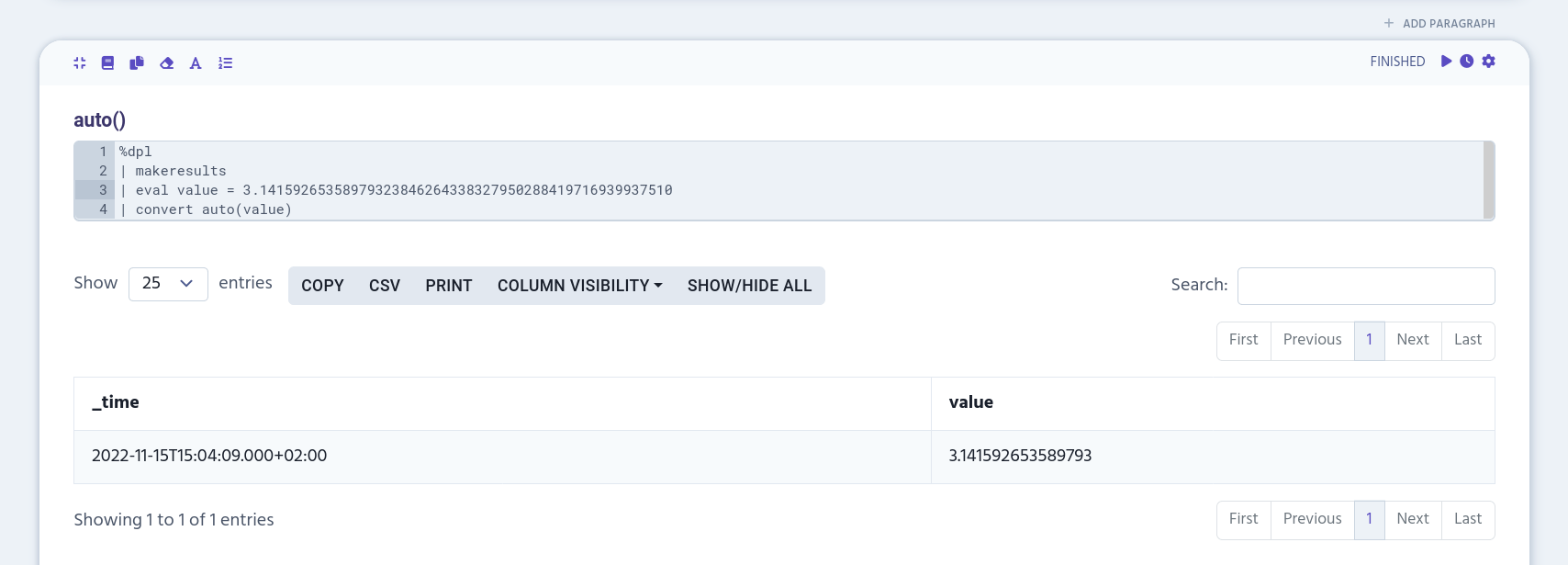
If the value can’t be converted, it will be skipped and won’t be converted at all.
ctime()
ctime() converts an epoch time to the ascii human-readable time. Use timeformat to specify the exact converting format.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval epochTime = 1664955774
| convert ctime(epochTime) as asciiTime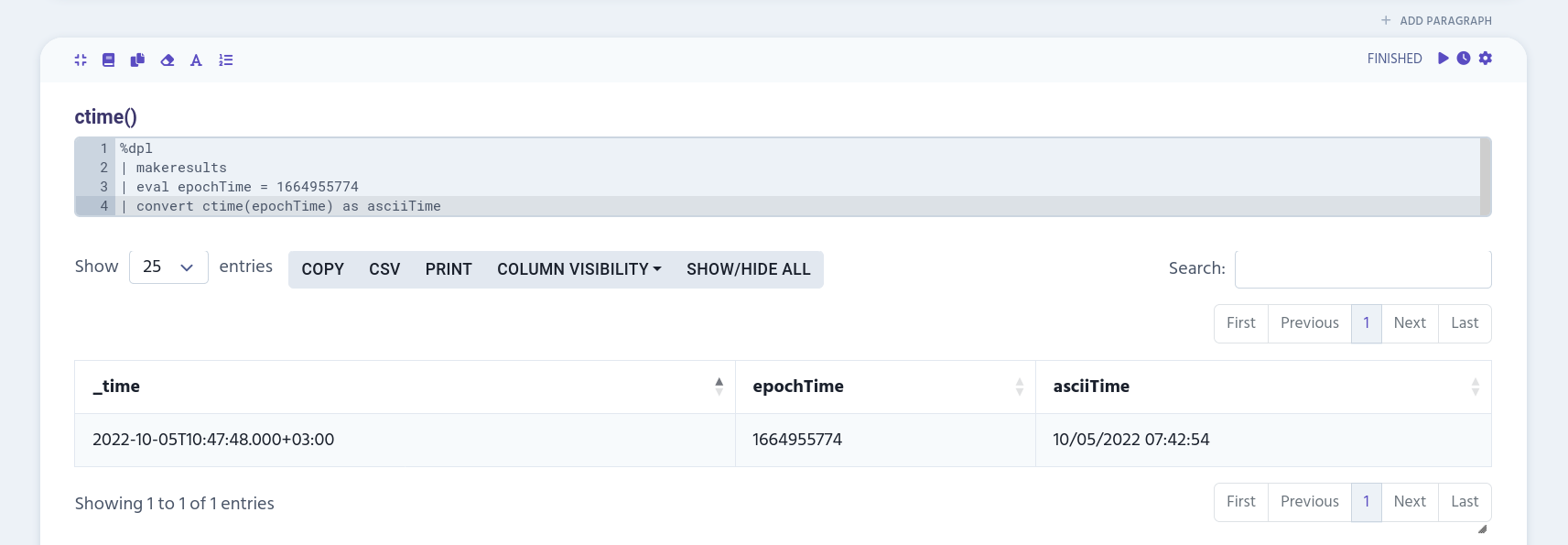
dur2sec()
dur2sec converts a duration format ([D+]HH:MM:SS) to seconds.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval time = "10:47:48"
| convert dur2sec(time) as durationTime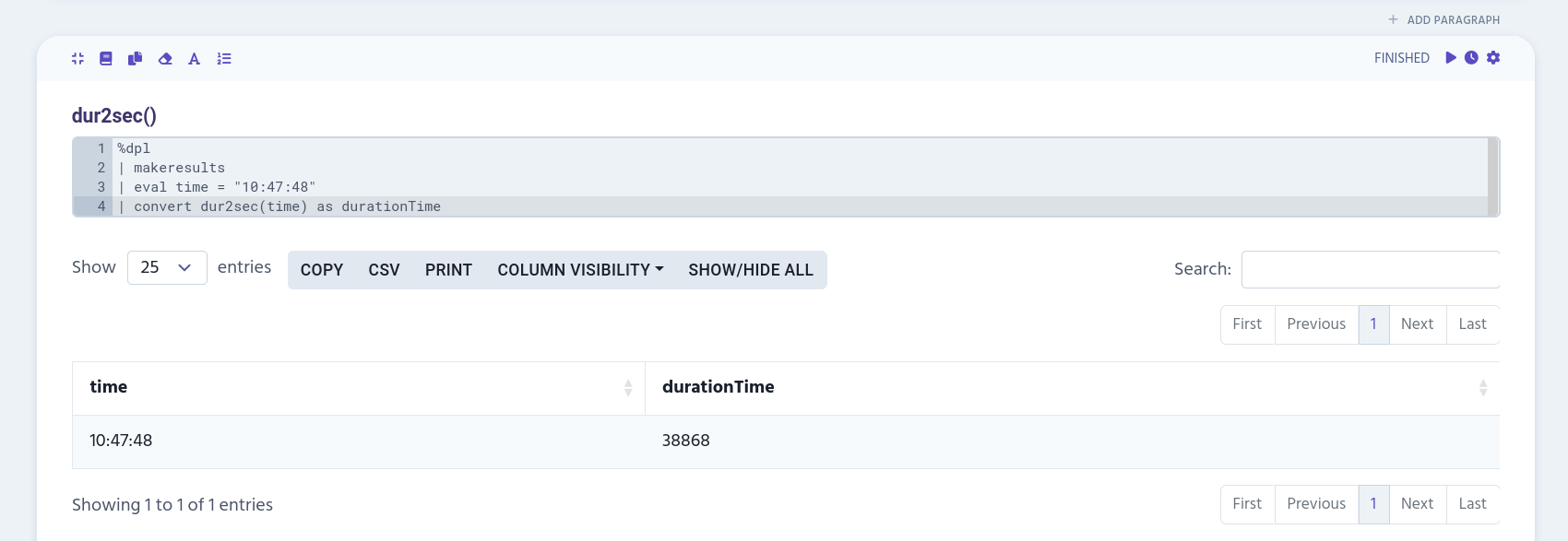
memk()
memk() converts the given value into kilobytes.
The function accepts positive numbers followed by k (kilobyte), m (megabyte) or g (gigabyte) letters. The value can be an integer or float. If there is no letter specified, the value is assumed to be kilobytes.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval kilobyte = "19k", megabyte = "19m", gigabyte ="19g"
| convert memk(kilobyte) memk(megabyte) memk(gigabyte)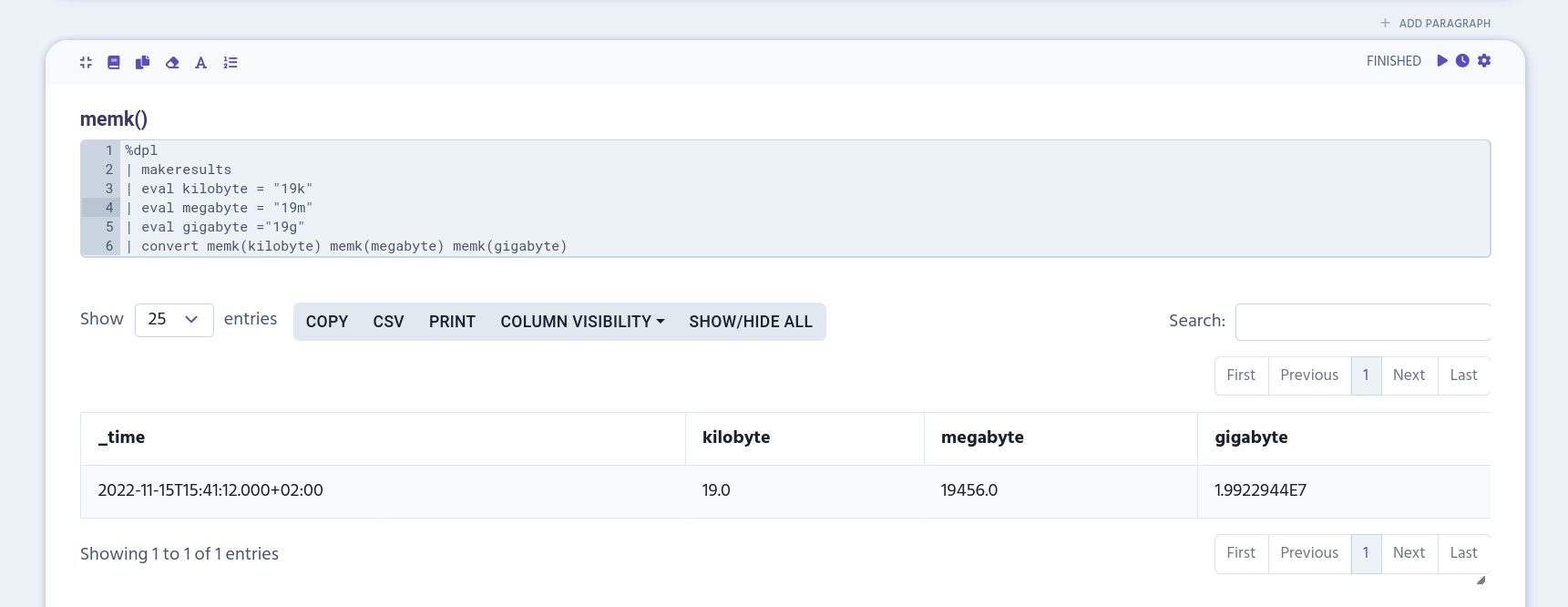
mktime()
mktime() converts the human-readable time into an epoch time.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval time = "10/05/2022 07:42:54"
| convert mktime(time) as epochTime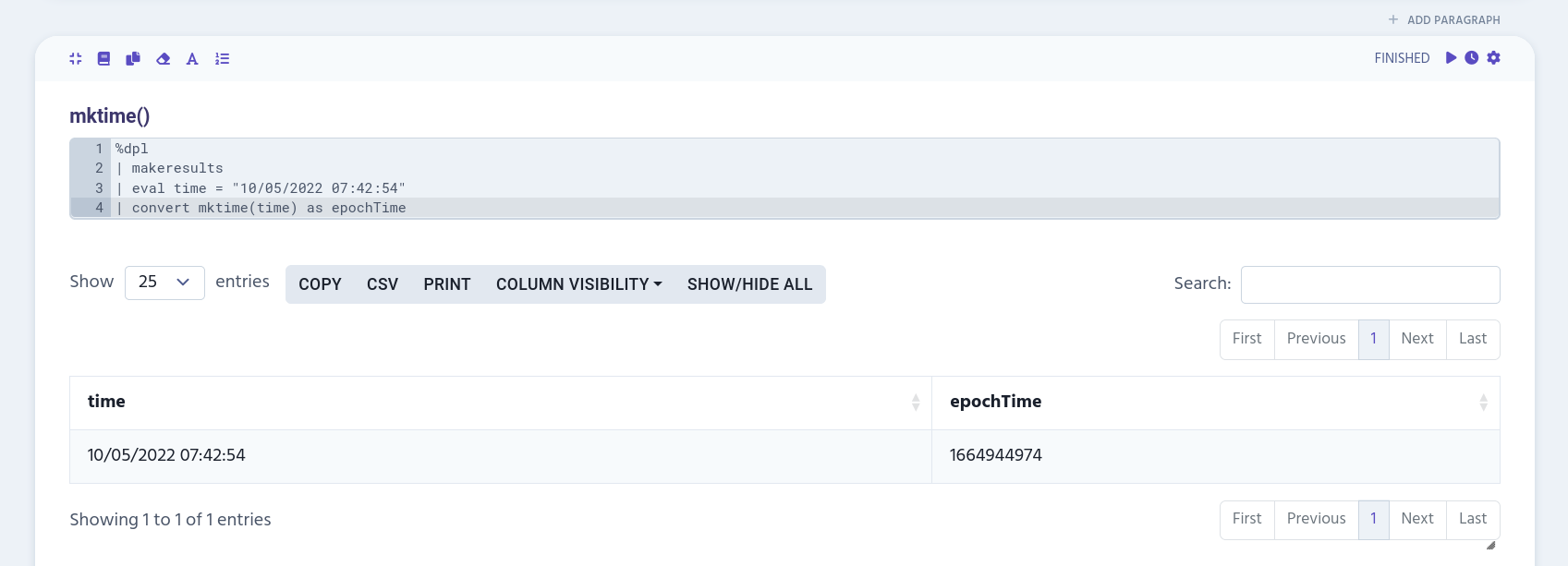
mstime()
mstime() converts the value into seconds.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval time = "03:58.000"
| convert mstime(time) as seconds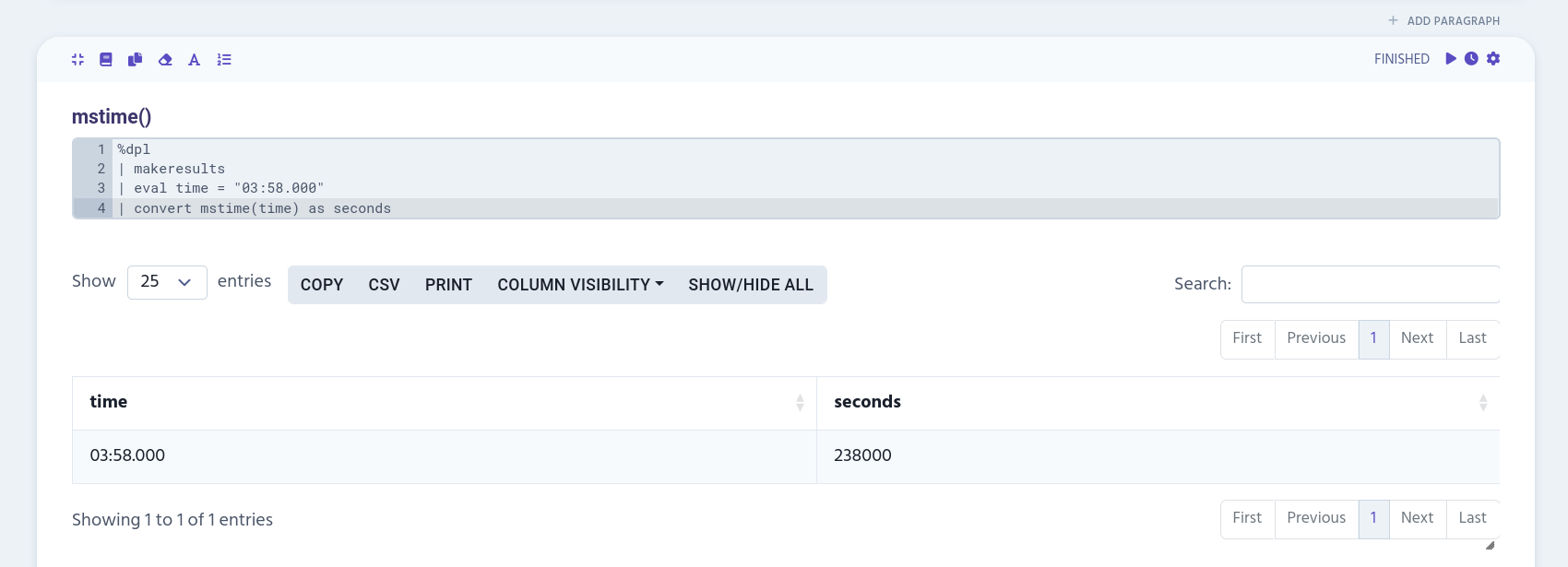
none()
none() prevents defined table columns to be converted when a wildcard is used.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval value1 = "1665558566", value2 = "1665558586", value3 = "seagull"
| convert ctime(*) none(value3)| Currently, wildcard doesn’t work in DPL. This will be fixed before the community release. |
num()
num() converts string to number. However, non-convertible values are removed.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval value = "12"
| convert num(value)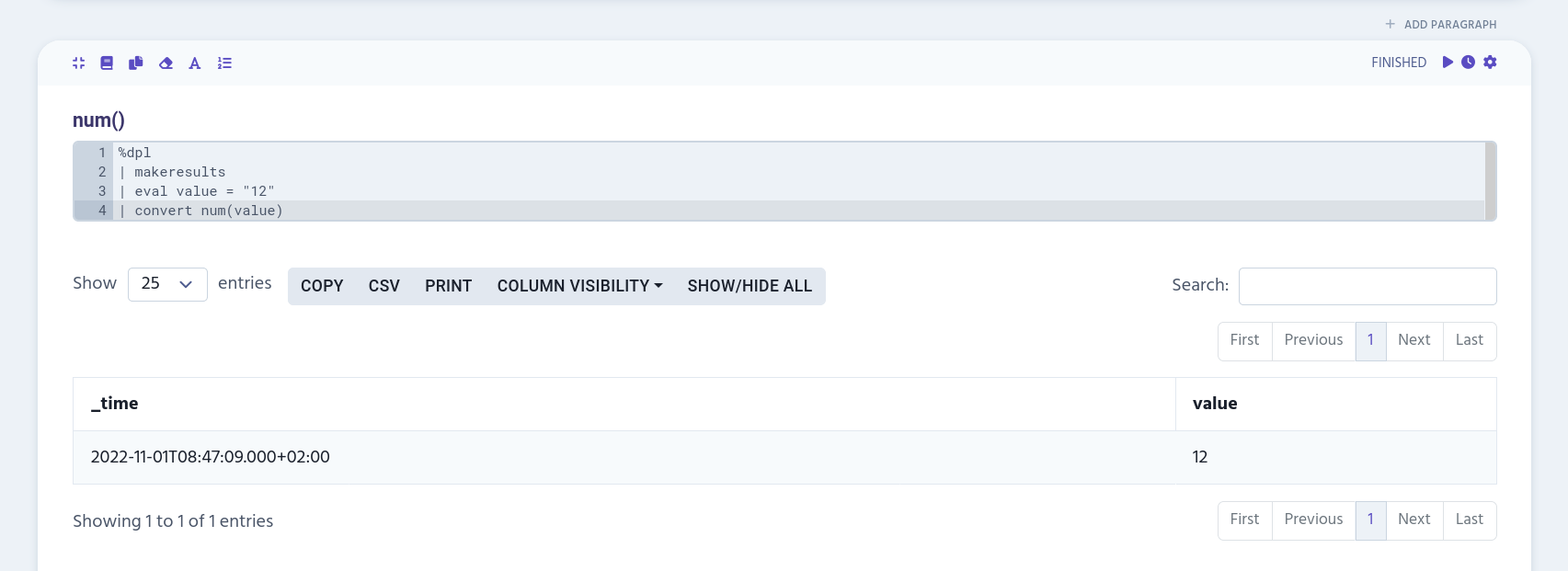
rmcomma()
rmcomma() omits all commas from the value.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval sales = "100,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000.00"
| convert rmcomma(sales)
rmunit()
rmunit() omits the first non-number character and other characters after it.
%dpl
| makeresults
| eval weight = "1000.00kg"
| convert rmunit(weight)|
|
|
Currently, |