rex
|
This command is experimental |
Definition
With rex command you can either extract data from columns based on a given regular expression, or replace characters in a column using sed expressions.
Syntax
| rex [field=<column-name>] ("<regex-expression>" [max_match=<integer>] [offset_field=<string>] | mode=sed "<sed-expression>")Examples
Use either a regular expression to extract data into a separate column or a sed expression to replace or substitute values that match with the regular expression.
To extract data, you can add only the regular expression after rex if you’re extracting from the _raw column.
index=sales_inventory earliest=-5y
| rex "(?<name>\w{8}-\w{4}-\w{4}-\w{4}-\w{12})"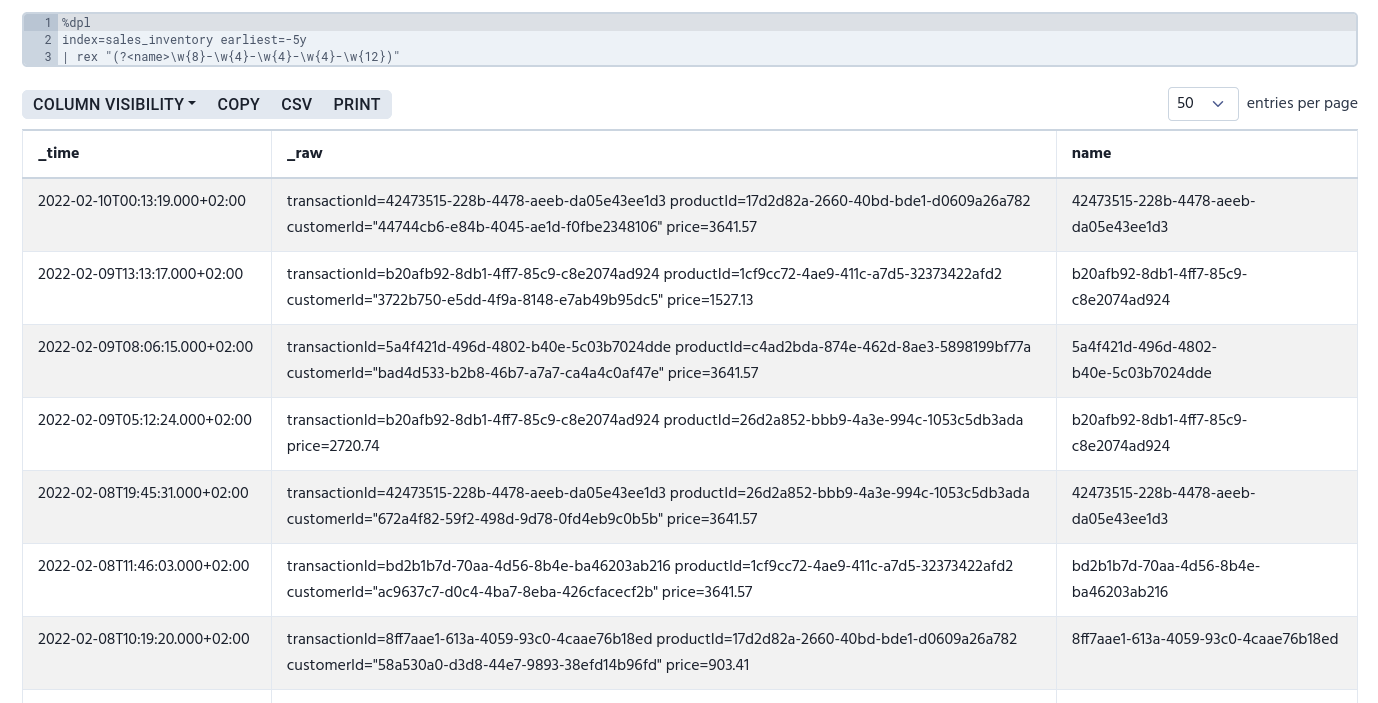
To replace values, use mode=sed and then add the sed expression.
| rex mode=sed "[s|y]/<regex-expression>/<replacement>/[g|Ng|N]"In the sed expression:
-
sreplaces strings -
yreplaces substitute characters -
/is a delimiter -
greplaces all -
Ngreplaces globally the Nth occurrence -
Nreplaces the Nth occurrence
| Replacing substitute characters isn’t currently supported. |
The following example uses sed expression to replace a certain ID with the product’s name for all matches.
index=sales_inventory earliest=-5y
| rex mode=sed "s/17d2d82a-2660-40bd-bde1-d0609a26a782/legendary book/g"|
Currently, sed expressions don’t work correctly. See the issue on GitHub. |
field
With field argument, you can define which column you want to extract data from.
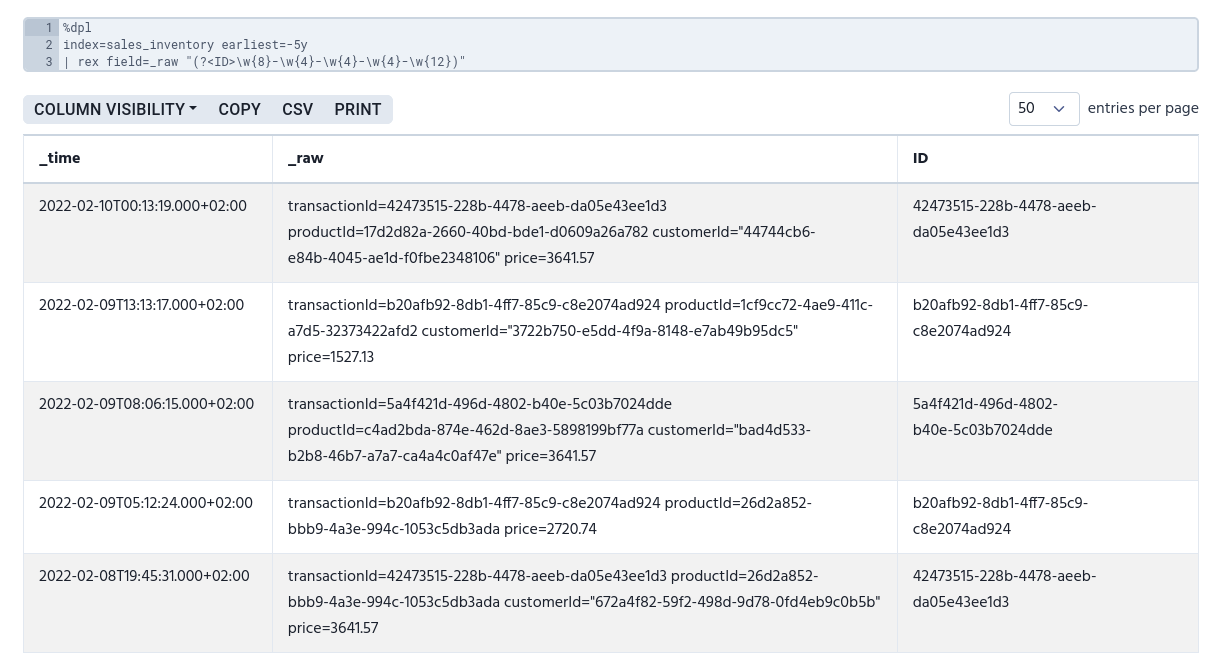
index=sales_inventory earliest=-5y
| rex field=_raw "(?<ID>\w{8}-\w{4}-\w{4}-\w{4}-\w{12})"